Chapter 6: Humanoid Control & Deployment
Overview
This chapter focuses on the practical aspects of controlling humanoid robots and deploying AI models onto them.
Objectives
- Understand the challenges of humanoid control.
- Learn about different control strategies.
- Explore the process of deploying AI models to physical hardware.
Core Content
Controlling a humanoid robot is a complex task that involves coordinating many joints to achieve stable locomotion and manipulation. This is often done using a whole-body control framework, which computes the torques for each joint required to achieve a desired motion while satisfying constraints such as balance and joint limits.
Deployment Considerations
Deploying an AI model to a physical robot requires several considerations:
- Real-time performance: The model must be able to run fast enough to control the robot in real-time. This often requires optimizing the model for the robot's onboard computer.
- Safety: The robot must operate safely in its environment, especially around humans. This requires implementing safety measures such as emergency stops and collision avoidance.
- Robustness: The model must be robust to sensor noise, actuator errors, and unexpected disturbances from the environment.
Examples
Conceptual Whole-Body Control
import numpy as np
from whole_body_controller import WholeBodyController
# Create a whole-body controller
wbc = WholeBodyController(robot_model)
# Define a task, e.g., move the hand to a target position
hand_target = np.array([0.5, 0.2, 1.0])
wbc.set_task("hand", "position", hand_target)
# Compute the required joint torques
joint_torques = wbc.compute_torques()
# Send the torques to the robot
robot.apply_torques(joint_torques)
Figures
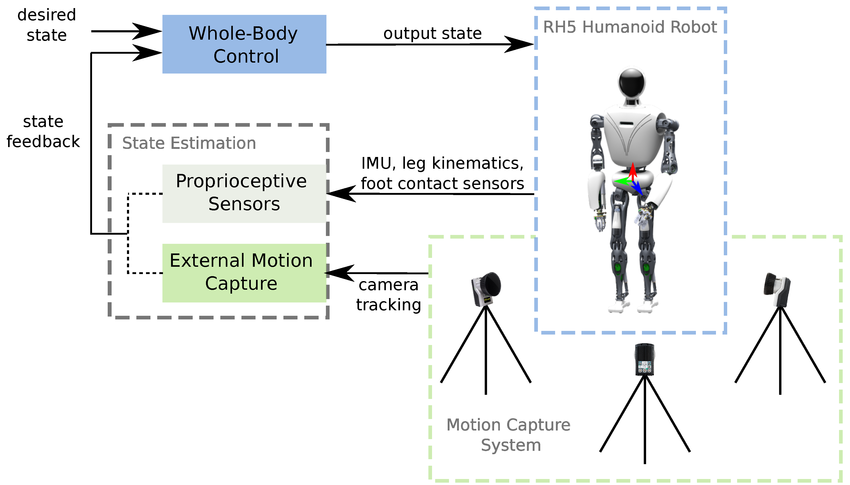
Figure 1: A simplified diagram of a whole-body control architecture for a humanoid robot.
Summary
This chapter discussed the challenges of humanoid control and the practical considerations for deploying AI models to physical hardware. We saw a conceptual example of a whole-body controller, which is a common approach for controlling complex humanoid robots. This concludes our introduction to the exciting world of Physical AI and humanoid robotics.